Table Of Content
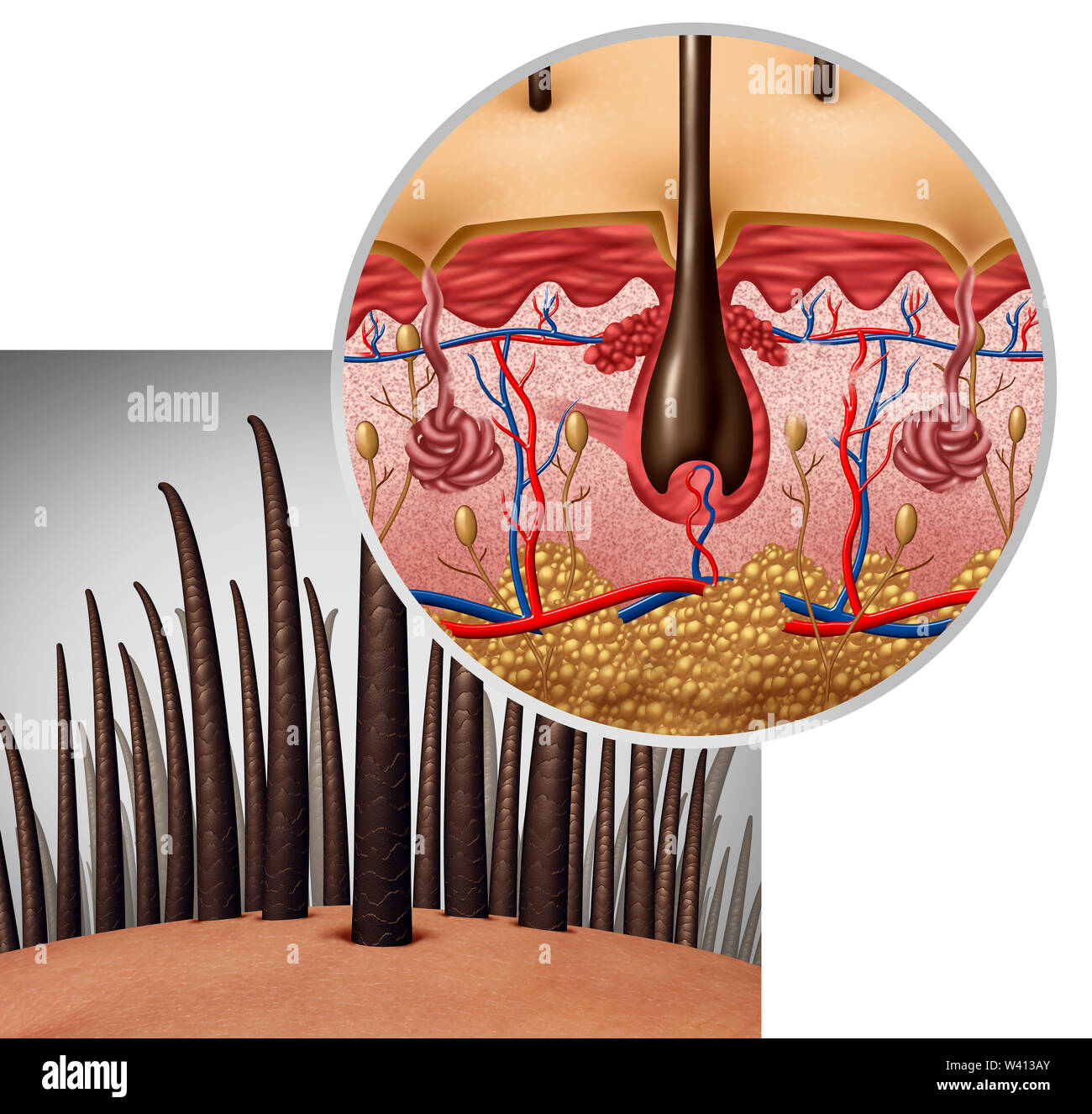
In this phase, growth slows down and the follicle shrinks. There are a handful of additional genes that have recently been identified and might play a role in regulating hair shape. Hair has many areas of clinical significance, which include diseases of hair loss, excess, alterations due to nutritional deficiencies, infectious causes, and effects of drug reactions. The ORS does not keratinize below the level of the isthmus (in contrast to the IRS).
What are the common conditions that affect hair follicles?
During the development of bullous peg (stages 5–8), the hair bulb and the main cell layers of the mature hair follicle are also formed [2–4, 6]. Hair grows and is eventually shed and replaced by new hair. The first is the anagen phase, during which cells divide rapidly at the root of the hair, pushing the hair shaft up and out. The length of this phase is measured in years, typically from 2 to 7 years. The catagen phase lasts only 2 to 3 weeks, and marks a transition from the hair follicle’s active growth.
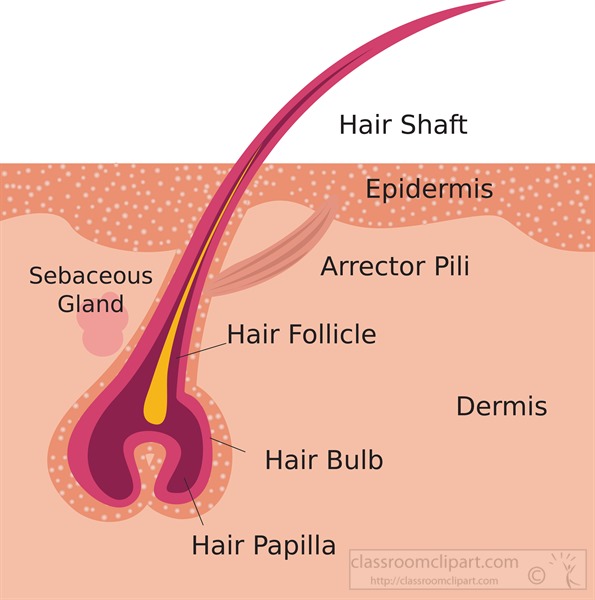
Hair Shaft
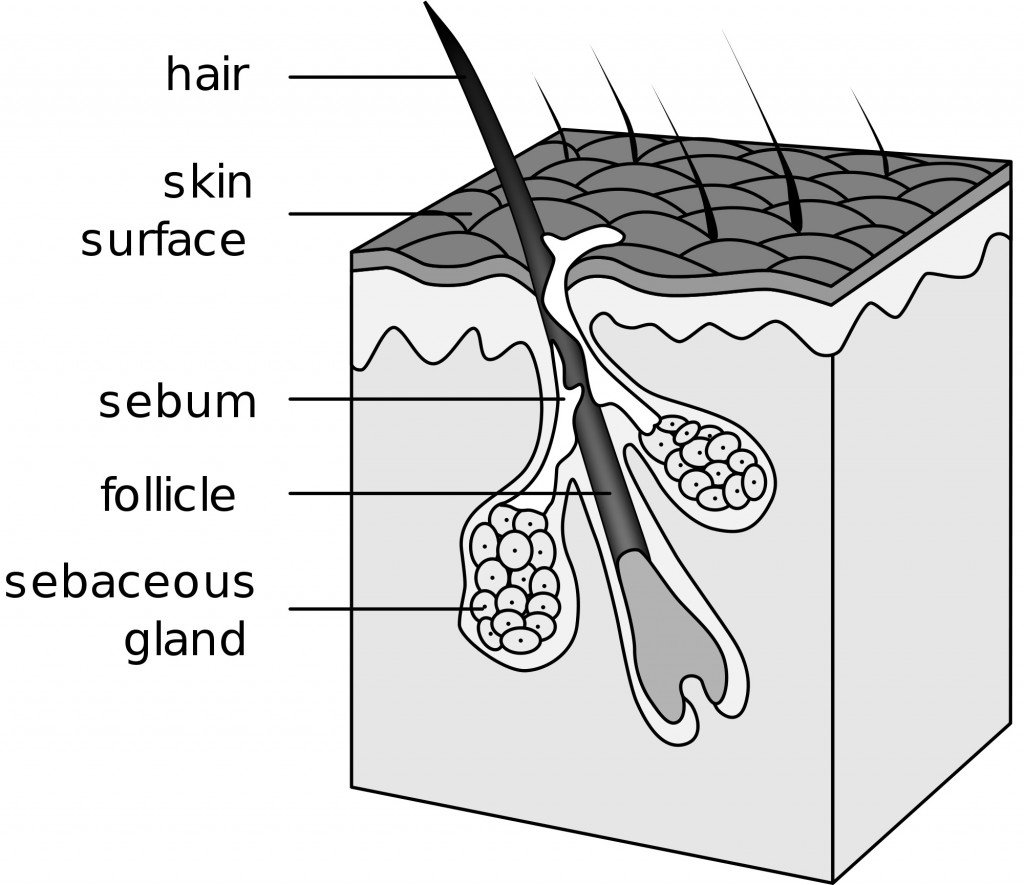
This results in the follicles not producing any new hairs. As more cells are created, the hair grows out of the skin and reaches the surface. Sebaceous glands near the hair follicles produce oil, which nourishes the hair and skin. If you damage your hair follicles after an injury, they can repair themselves and your hair will grow back. It could take up to four years before you see new hair growth out of damaged hair follicles, depending on the severity of your injury. Frequent injuries to your skin and hair follicles can produce scars, which make growing hair difficult.
KEGG enrichment analysis and PPI network analysis
Your hair follicle is made up of layers of cells within layers of your skin. These cells create a tube-like structure to hold your hair. A hair follicle looks like a long tube that holds your hair. It’s in the shape of a cylinder with a rounded bottom in your skin.
Lineage studies have proven that bulge cells are multipotent and that their progeny generate the new lower anagen hair follicle [21]. One of the most distinguishing features of stem cells is their slow-cycling nature, presumably to conserve their proliferative potential and to minimize DNA errors that could occur during replication. On entering the hair bulb matrix, they proliferate and undergo terminal differentiation to form the hair shaft and inner root sheath. They also migrate distally to form sebaceous glands and to proliferate in response to wounding [16, 20, 22].
Your hair follicles are responsible for growing hair, which happens in cycles of three distinct phases. It can be due to drugs, diet, hormone imbalances, altered mitotic activity, growth cycle abnormalities, among others. A thorough history, physical exam, hair pull test, daily hair counts, part width, clip tests to examine the hair shaft, hair growth windows, and hair pluck, and trichograms can all be used to diagnose hair disease. Scalp biopsies, hormone studies, and a potassium hydroxide examination for fungi may also need to be performed in certain cases.

Why Does Your Hair Curl In The Summer? A Chemist Explains The Science Behind Hair Structure - UMBC News
Why Does Your Hair Curl In The Summer? A Chemist Explains The Science Behind Hair Structure.
Posted: Fri, 11 Aug 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
The hair strands were oriented in the X-ray diffractometer with their long axis along qz. The 2-dimensional data were integrated and converted into line scans and fit for a quantitative analysis. Another function of hair follicle is giving color to your hair. Hair, like your skin, gets its color from a pigment called melanin [6]. There are two types of melanin - eumelanin and pheomelanin.
Recent Activity
It is interesting to note that differences are observed for the fraternal twins in Fig. This finding is in agreement with the expectation that individuals with similar genetics would share similar physical traits such as hair structure. Identical or monozygotic twins originate from one zygote during embryonic development, and they share 100% of their genetic material.
Hair texture (straight, curly) is determined by the shape and structure of the cortex, and to the extent that it is present, the medulla. The shape and structure of these layers are, in turn, determined by the shape of the hair follicle. Hair growth begins with the production of keratinocytes by the basal cells of the hair bulb.
The identical X-ray signals indicate that these products do not have an effect on the molecular structure of keratin and membranes deep inside the hair (within the resolution of our experiment). As expected, the identical twin pair shows almost identical hair structures whereas the fraternal pair exhibits distinct differences. Offspring receive half of their chromosomes from each parent, thus the genetic similarity between the parent and child pair is roughly the same as fraternal twins (Creasy et al., 2013).
Thermodynamically stable ionic liquid microemulsions pioneer pathways for topical delivery and peptide application - ScienceDirect.com
Thermodynamically stable ionic liquid microemulsions pioneer pathways for topical delivery and peptide application.
Posted: Thu, 02 Nov 2023 09:31:53 GMT [source]
Two articles had both hair follicle findings and litter size. Hair follicle, litter size, in vitro oocyte, and gene data performance traditional and network meta-analysis. Traditional meta-analysis of follicle density, cashmere fibre diameter, and yield. Traditional meta-analysis of melatonin’s effect on cashmere fibre length. Traditional meta-analysis of melatonin’s effect on goat litter size.