Table Of Content
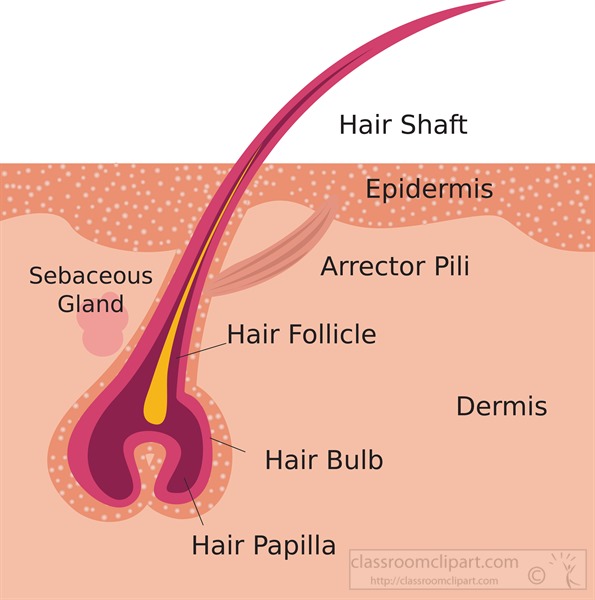
On the contrary, melatonin significantly reduces primary follicle density in goats (21, 22). It is necessary to analyze the effect of melatonin on goat hair follicles. This study provides theoretical guidance for the cashmere industry. The typical mammalian hair consists of the shaft, protruding above the skin, and the root, which is sunk in a pit (follicle) beneath the skin surface. Except for a few growing cells at the base of the root, the hair is dead tissue, composed of keratin and related proteins.
Hair bulb
The effects of GPR40 agonists on hair growth are mediated by ANGPTL4 - ScienceDirect.com
The effects of GPR40 agonists on hair growth are mediated by ANGPTL4.
Posted: Wed, 15 Mar 2023 09:06:35 GMT [source]
While common features can easily be identified in the 2D plots, subtle differences are visible, which are discussed in detail in the text. Adding melatonin in vitro can promote oocyte development in humans (14), mice (46), bovines (47), sheep (48), and swine (49). Our network meta-analysis results also showed that melatonin could promote goat oocyte development in vitro. First, embedded melatonin enters the bloodstream then passes through the blood-follicle barrier (BFB), where the concentration changes dramatically.
Alopecia areata

Java (version 1.8.0) was used to perform the trial sequential analysis (TSA) on the above data. At the end of the growth phase, the hair root separates from the papilla. Then a transitional phase called the catagen phase starts, lasting about two to four weeks. When the hair has separated completely from the papilla, the supply of blood is cut off in the final resting phase, which is also called the telogen phase. The hair is gradually pushed out of the skin and eventually falls out.
Tissue Preparation

The specimen of most individuals showed 3 distinct reflections at ∼90 Å, 46.5 Å and 27 Å, related to the properties of intermediate keratin filaments (B). In the direction along the hair fibre axis (qz), there are two major peaks that were consistent among all subjects, one narrow peak around 5.0 Å and one broader peak around 4.3 Å. Network meta-analysis data from the development of oocytes to blastocysts were used. R software (version 4.1.2) and the “coda,” “rjag,” and “gemtc” packages in JAGS (Just Another Gibbs Sampler, version 4.3.0) were used for the analysis. The results of the network meta-analysis were landscaped and processed using 3DMax software (version, 2023). The old hair falls out and paves the way for new hair to grow back from the roots all over again.
Beard hairs will arise once puberty is reached, with androgen hormones transforming the vellus hairs in this area into terminal hairs. While all hair samples showed these general features, differences between individuals were observed in the composition of the plasma membrane in the cell membrane complex. The cell membrane complex mainly consists of lipid mono- and bilayers. The corresponding scattering features correspond to a lamellar periodicity of about 45 Å, and rings at spacings of about 4.3 Å, characteristic of the order within the layers (Busson, Engstrom & Doucet, 1999). Both these features are observed in the 2-dimensional X-ray data of all individuals in Fig.
1. Hair growth cycle
Orange represents the pathway; green represents the genes. It protects the scalp from sunlight and keeps it warm in cold weather. I very much thank Seda Bilir Aksu for the excellent work of the figures in this chapter. The aim of this chapter is to enhance the knowledge of the complex anatomy and physiology of the hair in a simple manner (Table 1) [2, 5]. Your hair’s appearance is determined partly by the shape of your hair. If your hair has a circular circumference, it will be straight.
The dermal papilla consists of mesenchymal cells which function in the regulation of hair growth. This connective tissue structure also contains blood vessels and nerve endings which supply oxygen and nutrients to the root of the hair. The bulb encompasses the dermal papilla and the hair matrix. The dermal papilla consists of an egg-shaped accumulation of mesenchymal cells surrounded by ground substance that is rich in acid mucopolysaccharides (AMPs). The papilla protrudes into the hair bulb and is responsible for instigating and directing hair growth.
Here, stratum basale epithelial cells divide via mitosis to form the hair. A hair follicle is a tunnel-shaped structure in the epidermis (outer layer) of the skin. The root of the hair is made up of protein cells and is nourished by blood from nearby blood vessels.
Not all the follicles on your scalp are in the same phase at any given time. Different follicles go through the three different growth stages. How much of each hair type you have varies from person to person and also depends on your age and sex.
The infundibulum is the portion from the invagination of the epidermis to the level of opening of the sebaceous gland. The infundibulum is part of the pilosebaceous unit where sebum is expressed. The isthmus extends deeper to the level of insertion of the arrector pili muscle. The arrector pili muscle has attachments to the hair follicle and adjacent dermis.
Hair that is darker, thicker, and more visible to the human eye is called terminal hair. Areas of the body that appear to be hairless but have shorter, finer hairs that lack the medulla layer are called vellus hair. Neonates can be born with lanugo hair; fine hairs shed in utero or within the first weeks of life.[3] Club hair is fully keratinized hair that is fully formed in the telogen stage of the hair cycle. The only parts of the external surface of the body that are truly hairless are the palms and soles of the hands and feet, lips, labia minora, and glans penis. Nerve supply to the hair follicles is similar to that of the surrounding network of dermal nerves in that it is composed of both sensory afferents and autonomic sympathetic nerves. Sensory information from hair stimulation enhances tactile ability.
Finally, during the telogen phase, the hair follicle is at rest and no new growth occurs. At the end of this phase, which lasts about 2 to 4 months, another anagen phase begins. The basal cells in the hair matrix then produce a new hair follicle, which pushes the old hair out as the growth cycle repeats itself. Hair typically grows at the rate of 0.3 mm per day during the anagen phase. Hair loss occurs if there is more hair shed than what is replaced and can happen due to hormonal or dietary changes. Hair loss can also result from the aging process, or the influence of hormones.
However, at the level of the isthmus where the IRS disintegrates, the ORS keratinizes without forming granules (trichilemmal keratinization), which is similar to the keratinization of the hair cortex. When taking history in a patient with hair loss, it is imperative to determine what the patient is experiencing. Hair loss can refer to increased daily hair loss, which a clinician will elicit by asking if the patient notices more hair on his or her pillow or more hair in the shower after bathing.

No comments:
Post a Comment